







Home > News & Events : News > 2023.02 > Extremely polarized X rays have been detected at the Vela pulsar wind nebula by IXPE satellite.
February 10, 2023
Extremely polarized X rays have been detected at the Vela pulsar wind nebula by IXPE satellite.
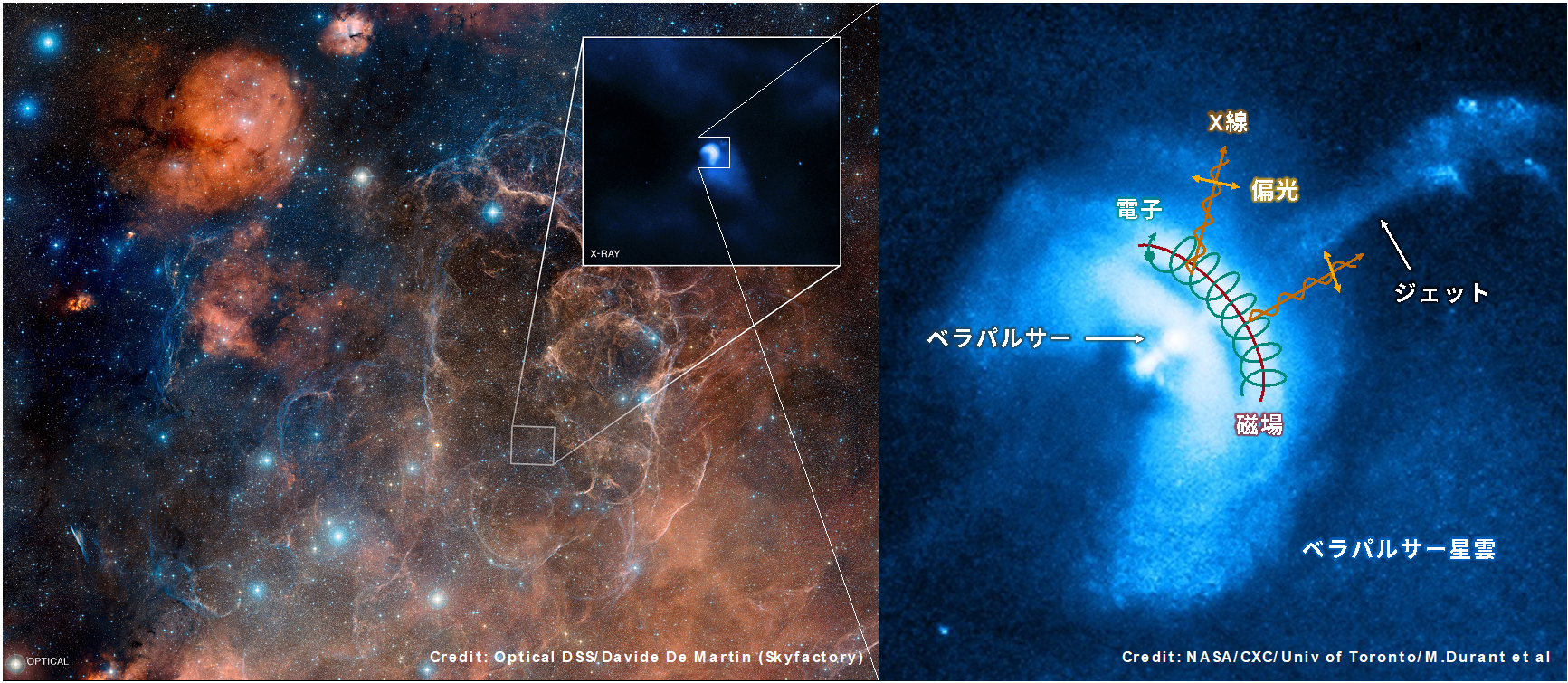
Pulsar wind nebulae (PWNs) are formed after heavy stars exploded and a neutron star called a pulsar remains near the center. The pulsar accelerates electrons and positrons, which strike the surrounding supernova remnant or interstellar medium. Then shock wave is generated and from the region X rays are emitted via synchrotron radiation.
The Vela pulsar wind nebula is one of the most famous PWNs. Though the X-ray map was obtained also for the Vela PWN, the polarization in the X-ray region has never been observed because of the difficulty of the detection in spite that the polarization observation can reveal the magnetic structure. The IXPE (Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer) satellite has broken through this situation and obtained the polarization map in the X-ray region for the first time in the world. Surprisingly, the degree of polarization exceeds 60% in an inner part of the nebula. It is approaching the theoretical limit of what can be produced by synchrotron emission and shows the existence of extremely ordered magnetic fields. Members of the IXPE at Yamagata University also participated in the data analysis and contributed to this scientific achievement. For more details, please see the paper published in Nature.
Related Links